Business leaders have a legislative duty to acquire and maintain up-to-date knowledge of work health and safety matters relevant to the nature of their operations. But without any visibility of the health and safety prosecutions that have occurred, it can be hard to grasp what could go wrong within your operations.
With a little context, you have an opportunity to reflect on current practices. This can help to ensure that reasonably practicable controls have been established, and to ensure ‘like’ or ‘now foreseeable’ incidents are less likely to occur within the workplace.
‘Reasonably practicable’ means that you should consider the likelihood and degree of harm of a hazard or risk. Whilst there may not have previously been an incident at your workplace, if a significant incident has occurred across your industry, you should be aware of it.
Each year, Action OHS Consulting collates and reviews the data available from both WorkSafe Victoria and SafeWork NSW. Used effectively, this information should support you to influence key stakeholders within your organisation, and assist your business to make informed decisions with respect to their health and safety program.
The prosecution data has been collated from:
- WorkSafe Victoria Prosecution Data
- SafeWork NSW Prosecution Data (at the time of writing, data was provided by SafeWork NSW up until May 2022)
This article provides an overview of the prosecutions from 2015 through to the 2022 calendar years.
Prosecutions: Numbers and related legislation
The 2022 calendar year saw a total of 115 prosecutions against the Victorian health and safety legislation, whilst in NSW at May 2022** the number of prosecutions was 17.
***Note at the time when this report was produced, SafeWork NSW website provided an overview of prosecutions up to May 2022 – once this changes, this report will be updated accordingly***
When compared to the previous year, there has been a 20% increase in Victoria. This is compared to a 54% increase in Victoria the CY2021 when compared to CY2020. The CY2020 reduction may be attributed to resourcing during COVID along with lockdown restrictions.
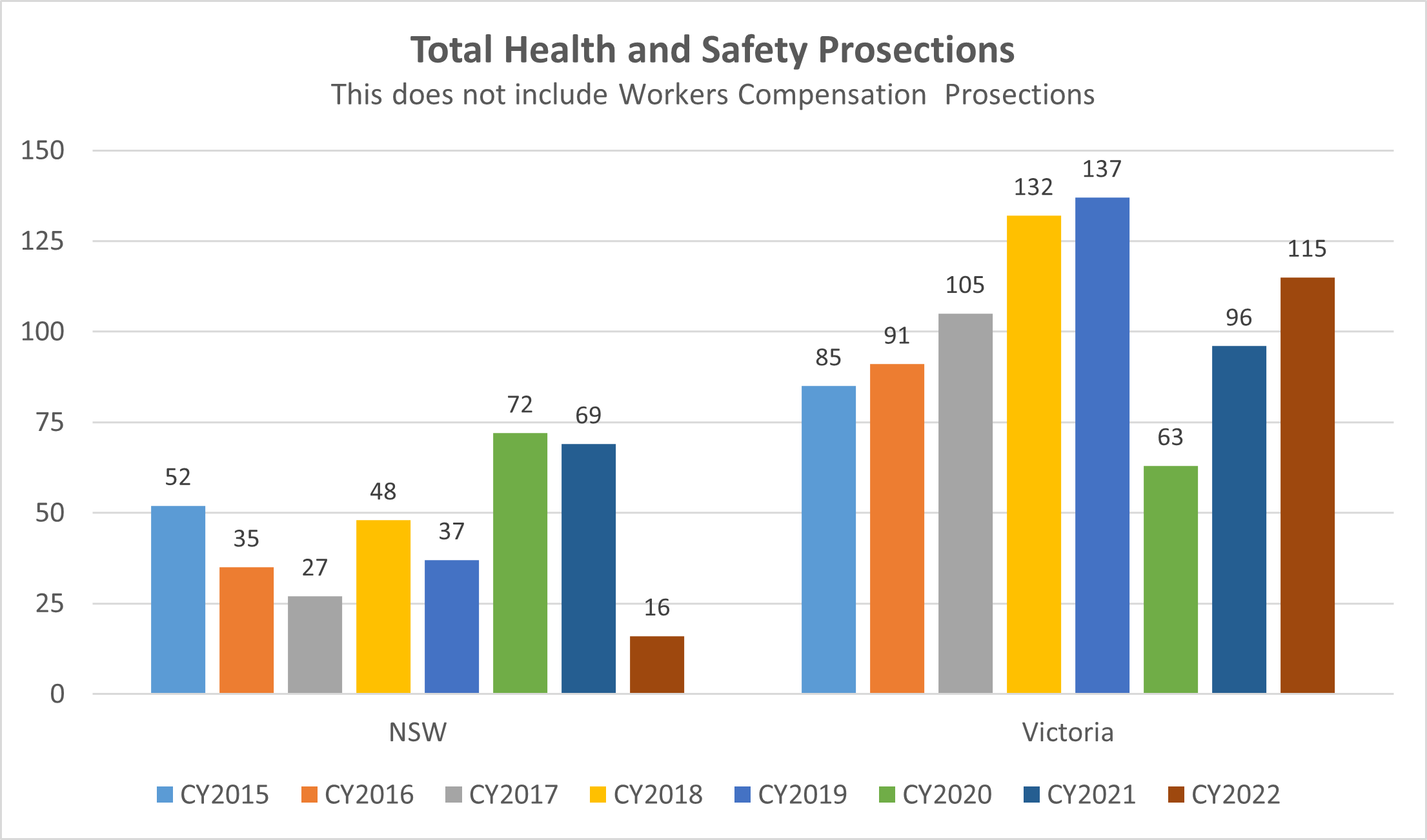
Within Victoria:
- 96 prosecutions were recorded against the Occupational Health and Safety Act 2004 only
- 18 prosecutions involved both the Occupational Health and Safety Act 2004 and the Occupational Health and Safety Regulations 2017
- 1 prosecution involved the Occupational Health and Safety Act 2004; Occupational Health and Safety Regulations 2017; Dangerous Goods Act 1985
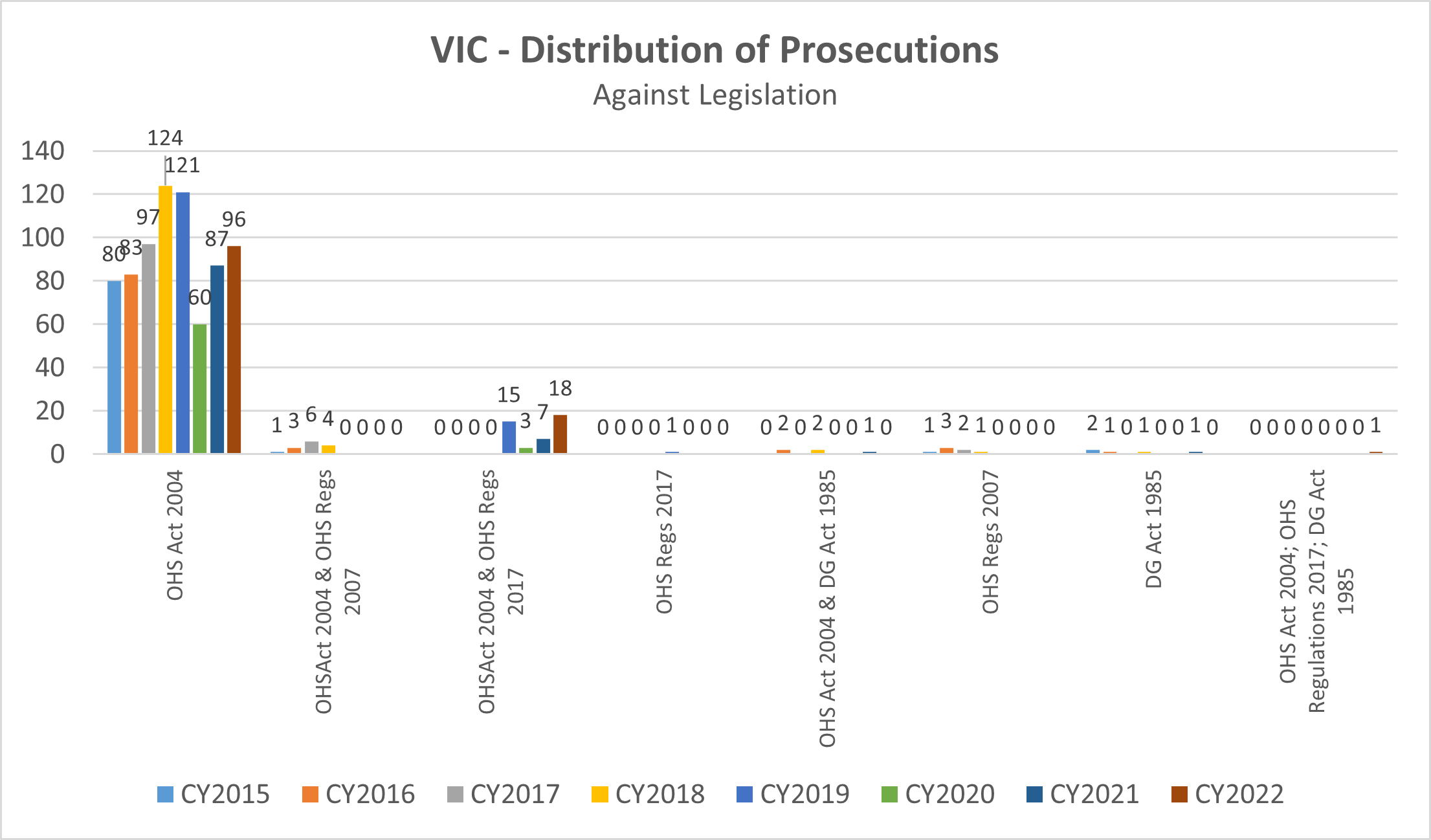
Consistent with previous years, zero prosecutions were against the 2007 version of the Occupational Health and Safety Regulations which were updated in 2017.
Within NSW up to May 2022:
- 14 prosecutions were recorded against the Work Health and Safety Act 2011 only
- 1 prosecution was recorded against the Work Health and Safety Regulation 2017 only
- 1 prosecution involved both Work Health and Safety Act 2011 & Work Health and Safety Regulation 2017
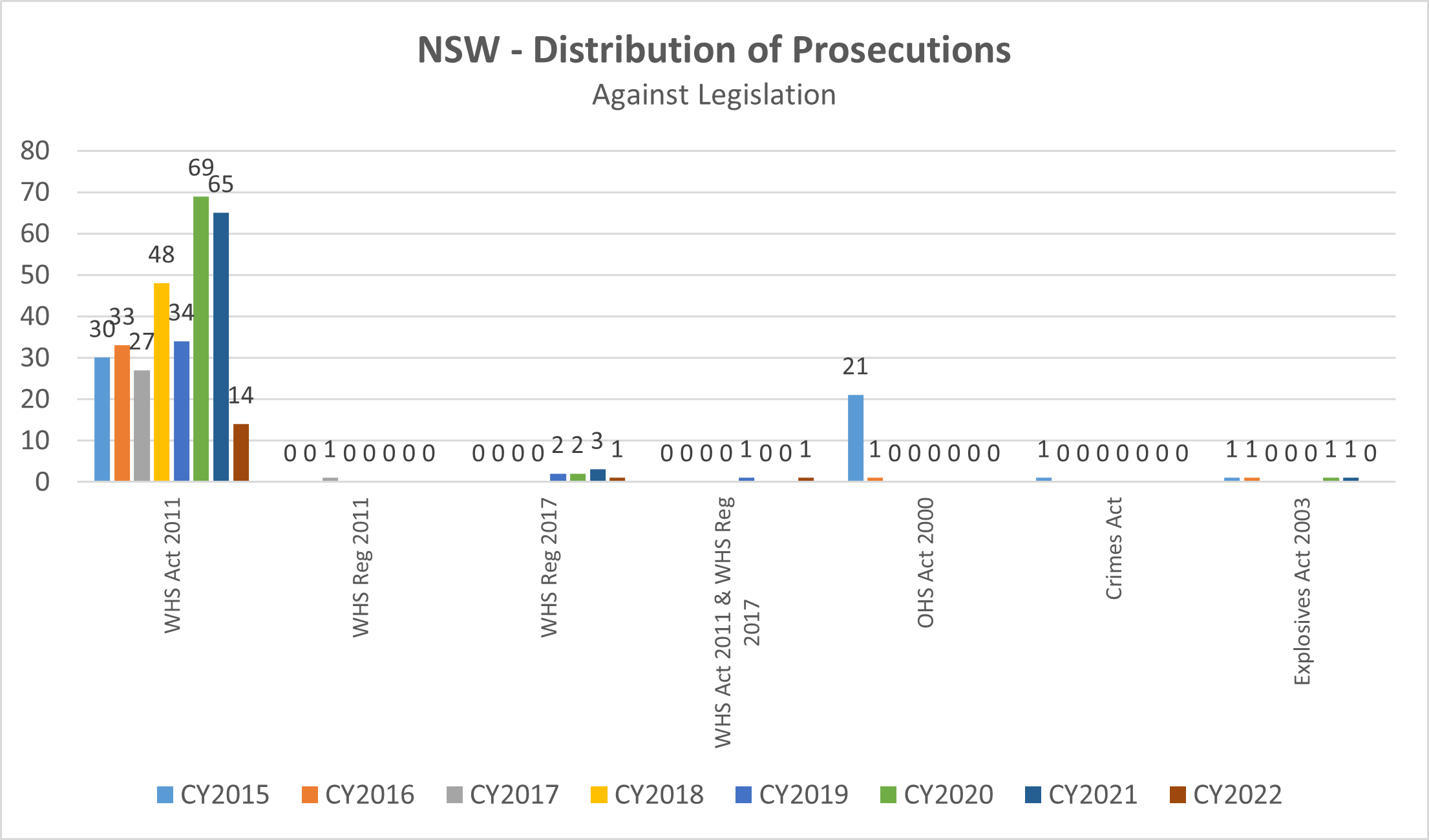
Prosecution timeframes
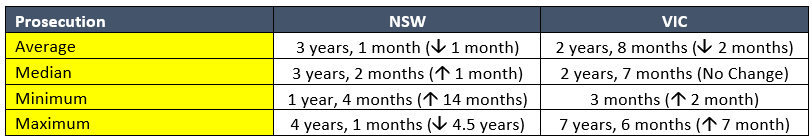
The table below lists the timeframe for the prosecution’s outcomes from 2022 when measured against the date of the offence.
Table 1: Timeframe between date of offence and the prosecution outcome, for the 2022 prosecution outcomes reported by SafeWork NSW & WorkSafe Victoria. Bracketed numbers represent the increase / decrease from 2021.
Health and safety fines
Year on year, the average fine and median fine in Victoria and in NSW remained consistent with previous years. The average and median fines were greater in NSW, when compared to Victoria.

WorkSafe Victoria issued five Enforceable Undertakings in 2022 which equates to 4% of prosecutions. This aligns with the percentage of prosecutions that resulted in Enforceable Undertaking issued in 2021.
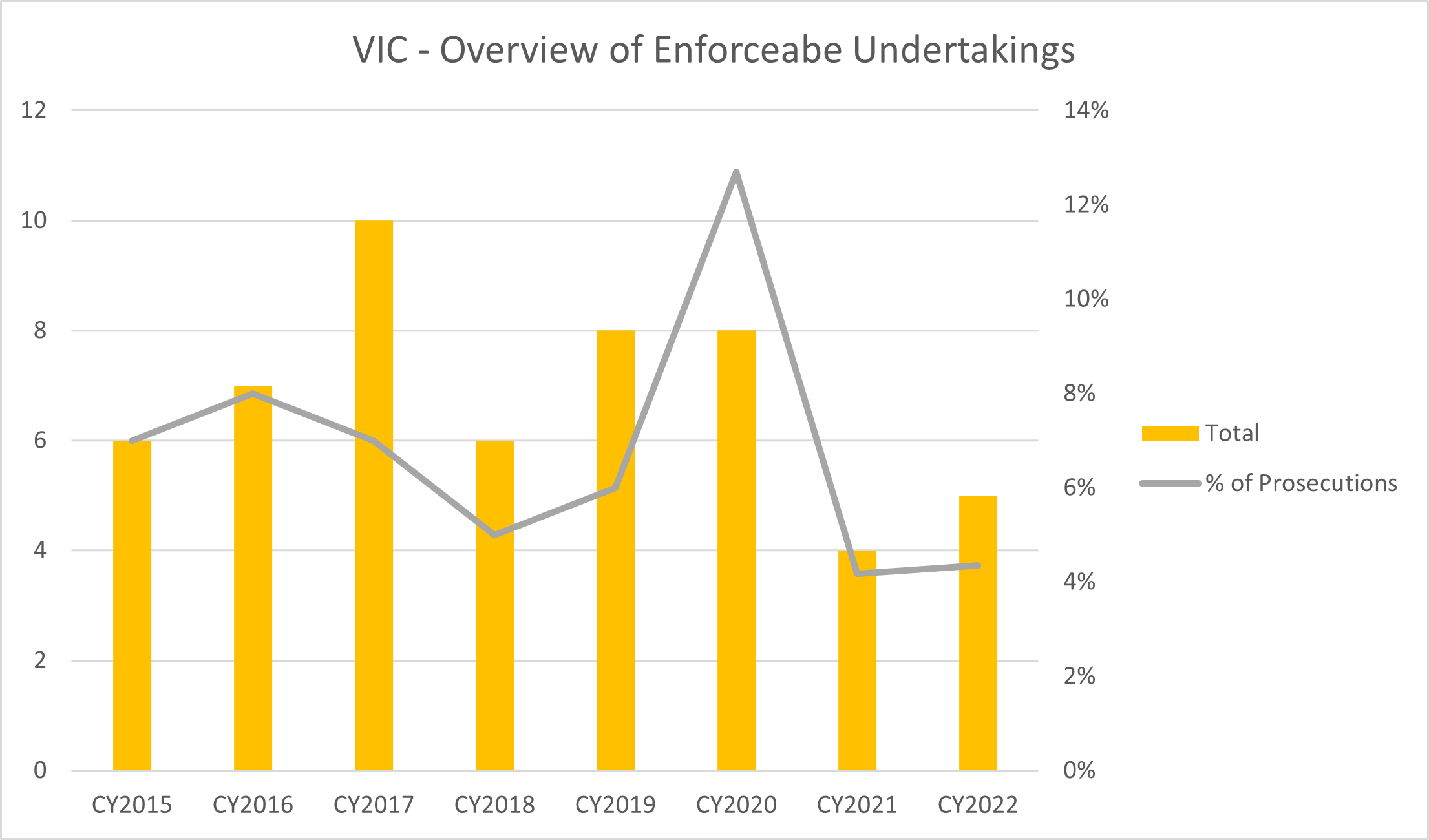
An ‘enforceable undertaking’ (EU) is a legally binding agreement between WorkSafe Victoria and the employer. The employer is obliged to carry out the specific activities outlined in the agreed undertaking. EUs will typically guide and direct the business being prosecuted to improve its health and safety program.
Health and safety fines: Maximum issued
With respect to fines, the maximum fines for Victoria was slightly above 2021, however, there was a significant decrease in NSW year on year. This number may increase once prosecutions from June to December 2022 are presented.

The maximum fines issued to a business were associated with the following events:
Victoria: The offender manufacture and supply liquid and dry bulk road tankers and employ approximately 40 – 50 workers on the factory floor. Australian Industry Group Training Services Pty Ltd (AIGTS) employed an engineering fabrication apprentice.
An external Safety Consultant completed an audit on a new workplace environment during August 2018, whilst production had commenced the setup of the new factory was still not complete. The audit identified several opportunities for improvement.
On 24 September 2018, the apprentice attended at the workplace for work for the first time. The apprentice was 20 years of age, a trainee welder and did not have a trade qualification.
On 4 October 2018, the apprentice was asked to perform a ‘cleaning out task’ inside a tanker. The previous day an employee of the offender had left a Welder and a Wire Feeder inside the tanker. It remained there overnight. The Wire Feeder had fallen into a state of disrepair. As a result of that defect, over which the offender had management and control, Argon gas was able to flow into the tanker overnight, reducing oxygen in it. The apprentice died from asphyxiation after entering the tanker to perform the cleaning out work.
Workers at the workplace extracted the apprentice from the tanker and performed CPR. Emergency Services arrived within about five minutes after the apprentice was extracted. The apprentice died at the scene.
The offender pleaded guilty and was with conviction sentenced to pay a fine of $600,000. The Court indicated that but for its guilty plea, the offender would have been convicted and fined $800,000.
NSW: On 12 April 2019, a worker was operating a John Heine Power Press when his chair slipped and his foot connected with the unguarded lever, activating the Press, which crushed his right-hand fingers.
After a SafeWork NSW investigation, the defendant, was charged with a breach of section 32/19(1) and 38(1) of the Work Health and Safety Act 2011.
On 22 February 2022, the defendant was convicted by the District Court and fined $135,000 for the breach of section 32/19(1) of the Act and $12,000 for the breach of section 38 of the Act.
It is not just businesses being prosecuted in relation to health and safety breaches
Health and safety prosecutions are not limited to corporations. In 2022, 10% and 13% of prosecutions were issued to workers in Victoria and NSW respectively – equating to 12 and 2 prosecutions respectively
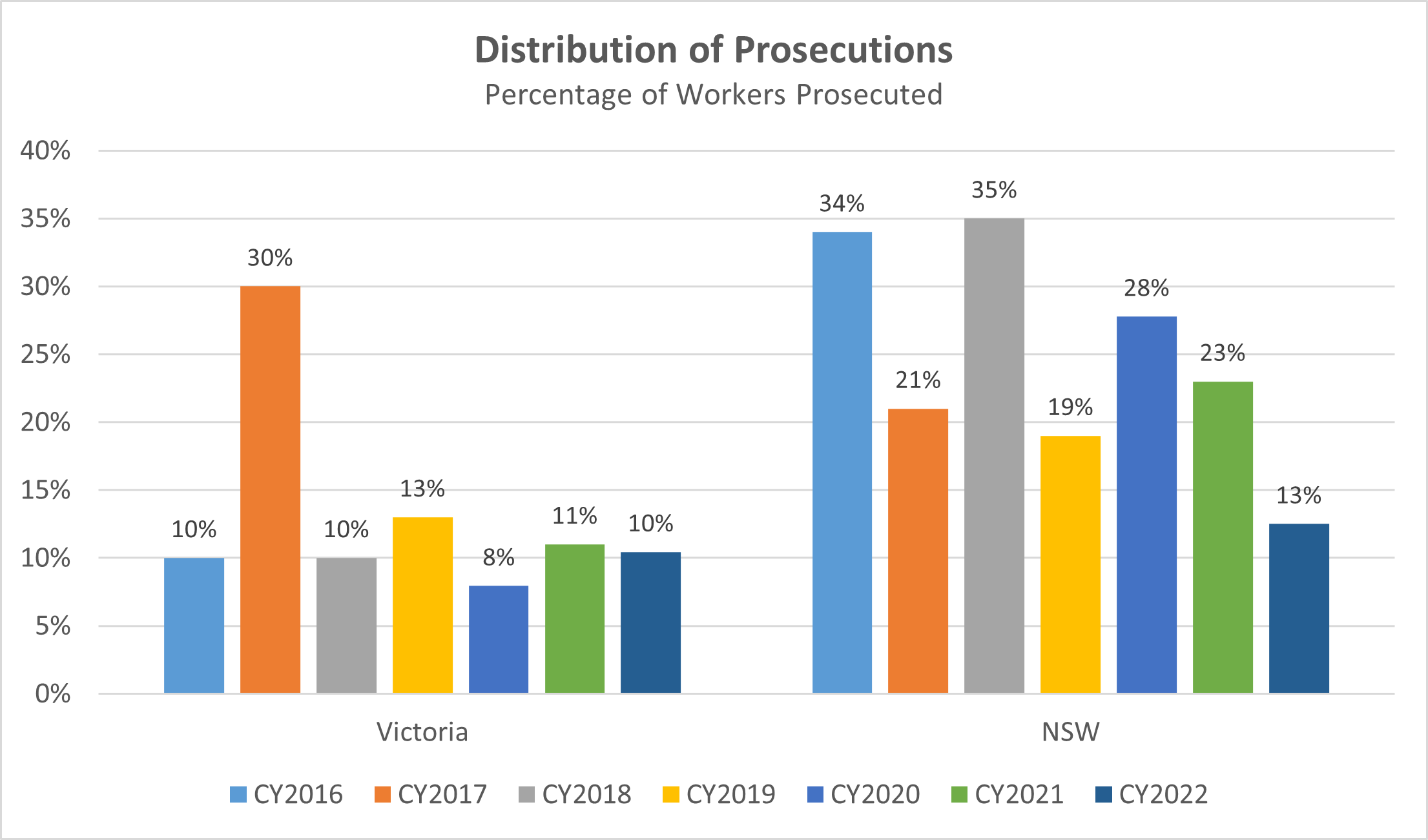
The maximum fine issued to workers in Victoria and NSW in 2021 was $70,000 and $60,000 respectively. Whilst the average fine in Victoria and NSW was $15,875 and $48,750 respectively.
Prosecutions: What is the cause and where are the gaps?
With respect to the criteria/codes that lead to the prosecution – of the 48 criteria that was referenced, with 13 criteria associated with more than 10% of the prosecutions in 2022. As defined by WorkSafe Victoria, these are outlined below.
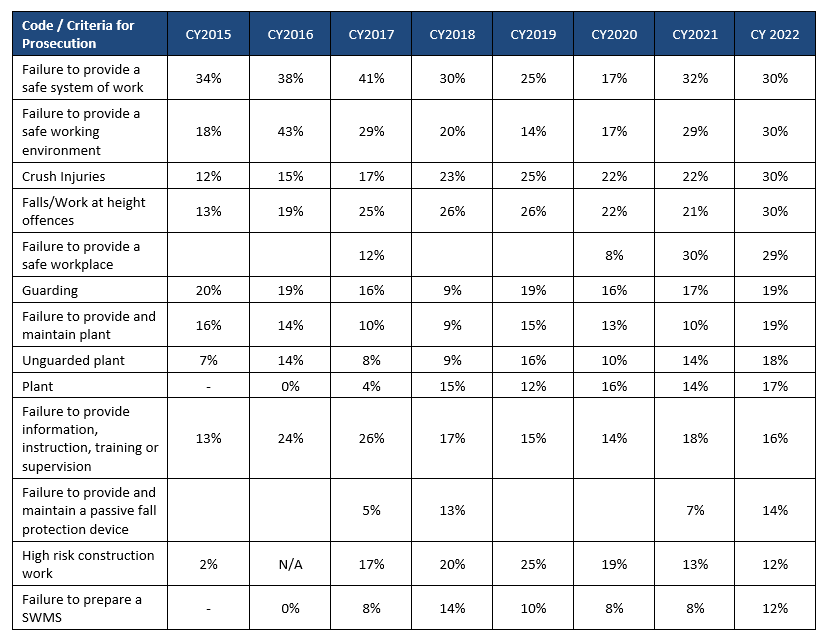
These criteria are relatively consistent since 2015.
‘Failure to provide a safe system of work”’ continues to places a clear duty on all workplaces to understand their operations, the hazards associated with their work, and ensure that the established controls are implemented.
Other noteworthy criteria includes:
- 1. The re-introduction of “Failure to provide and maintain a passive fall protection device” to the list. Whilst “Falls/Work at height offences” have been consistent, this new addition explicitly calls out the expectation the regulator is placing on organisations who conduct work at heights.
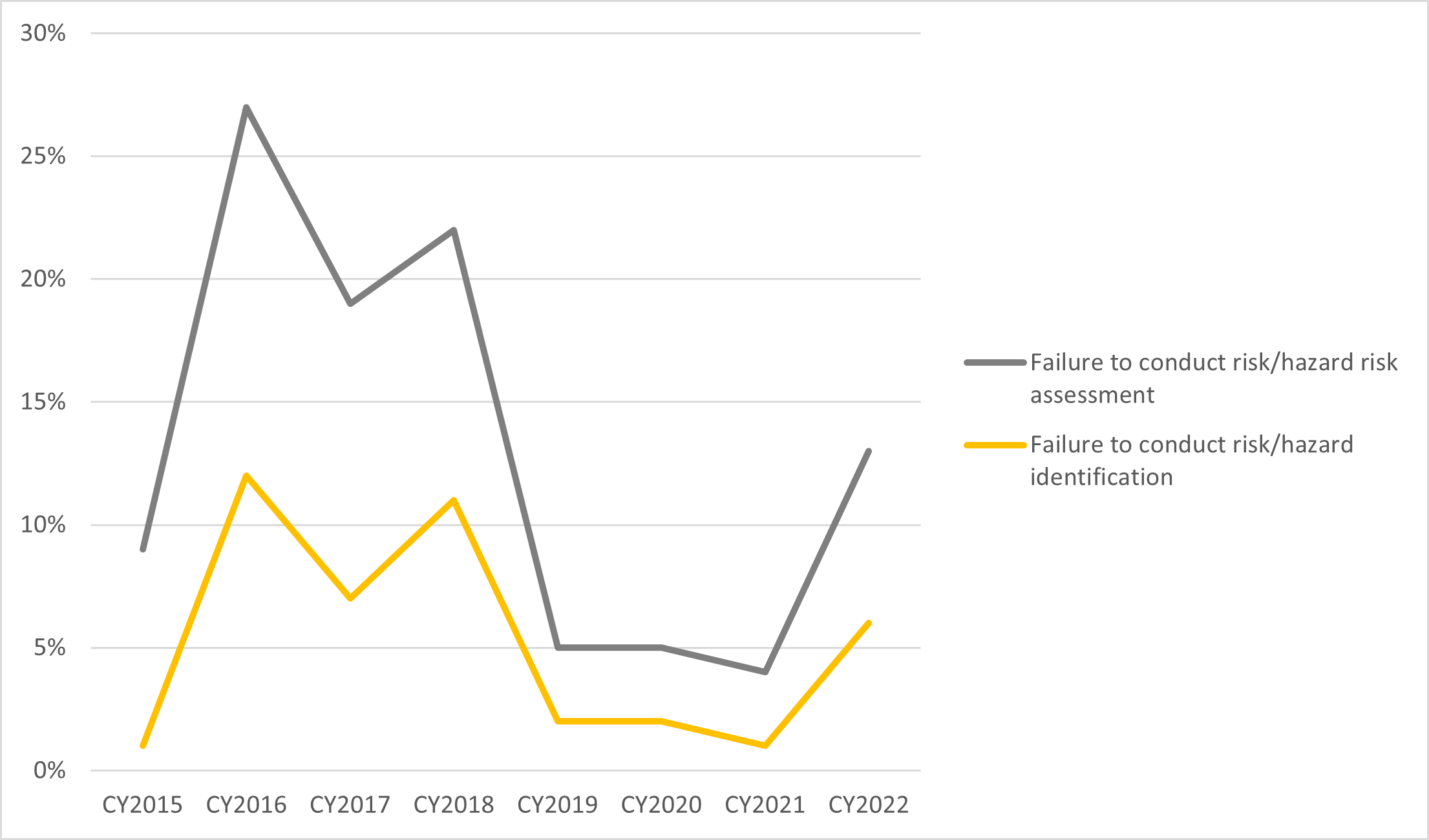
- Slight increase in prosecutions related to failure to conduct risk/hazard identification or risk assessment following a drop off in CY2019 to CY2021:
Health check
Action OHS Consulting, in collaboration with its sister-company Safety Champion Software, has developed a self-assessment tool: Safety Champion Impact Assessment. This tool has been designed to support businesses to understand potential points of failure, allowing them to proactively improve their health and safety program.
We plan to make this tool accessible up until 31 March 2023.
START SAFETY CHAMPION IMPACT ASSESSMENT
Free consulting support
As part of the WorkSafe Victoria OHS Essentials Program, businesses with operations in Victoria, may be eligible for three (3) OHS Consulting Support sessions delivered over 12 months by an Action OHS Consulting consultant. These sessions are designed to guide businesses on how to deliver on the legal OHS duties and obligations.
Free webinar support
Action OHS Consulting developed and delivered a four-part webinar series providing direction on how businesses can best manage their legal obligations associated with health and safety.
The good news is that it is free for you to download.
Key takeaways
To allow better and more informed decisions to be made, businesses must have established processes to understand how effectively their health and safety program has been implemented.
The Health and Safety Legislation adopts a self-regulated risk-based approach. This means businesses and their leaders are required to understand what could foreseeably go wrong within their operations, and then establish reasonably practicable controls to minimise the likelihood or severity of such events occurring. The intention; is to protect workers, contractors, customers and visitors from harm.
This require leaders to be real. It requires them to appreciate that safety as documented by your policy and procedure manual, may not reflect work as completed operationally.
Put simply, this leads to a requirement for workplaces to actively:
- Ensure that your safety program is easy to access and understand, and importantly relevant to your operations. Strongly consider implementing safety software such as Safety Champion, to help ensure that scheduled tasks are completed, and that workers can easily report incidents and/or hazards. Ensuring that you have visibility and read access to this information, will assist you to proactively prevent incidents from occurring in the future.
- List all the ways your workers could get hurt, and document what you have put in place to stop this from happening. Start by listing the “Top 5” hazards – focusing on those which could cause the most serious harm. Do this in consultation with a selection of workers who hold different roles within your business. If you identify things that you could improve and/or do better, this is not bad, in fact, it is the point of the exercise.
- Continue to consult. Have regular structured and unstructured conversations with your team regarding the controls you have established.
- Build competency. Ensure that you have an induction program that includes an overview of your safety program and the operational activities that the worker will undertake. Consider assigning a buddy to new and/or young workers.
- Ensure your safety program is sustainable. Don’t rely on just one person. Spreadsheets and folders can be effective if you are organised, however, are difficult to maintain visibility when tasks are due – or more importantly, when tasks are missed. Again, this is where software programs like Safety Champion Software will support your organisation, providing visibility of your health and safety program in real-time, remind you when deadlines and key milestones approach, and provide you with access to data to make data-based decisions.
- Consider safety as part of your procurement process. Before you buy anything, consider the safety implications. Don’t limit this to equipment, machinery, computers – extended this to services as well. Don’t make safety an afterthought.
We would be interested to hear your thoughts, questions or concerns.
If like us, you would like to interrogate data, we would be more than happy to share an unlocked copy of the data with you
We would be interested to hear your thoughts, questions or concerns.
If like us, you would like to interrogate data, we would be more than happy to share an unlocked copy of the data with you – simply Contact Us.
Authors: Craig Salter, Nicole Watkins.

